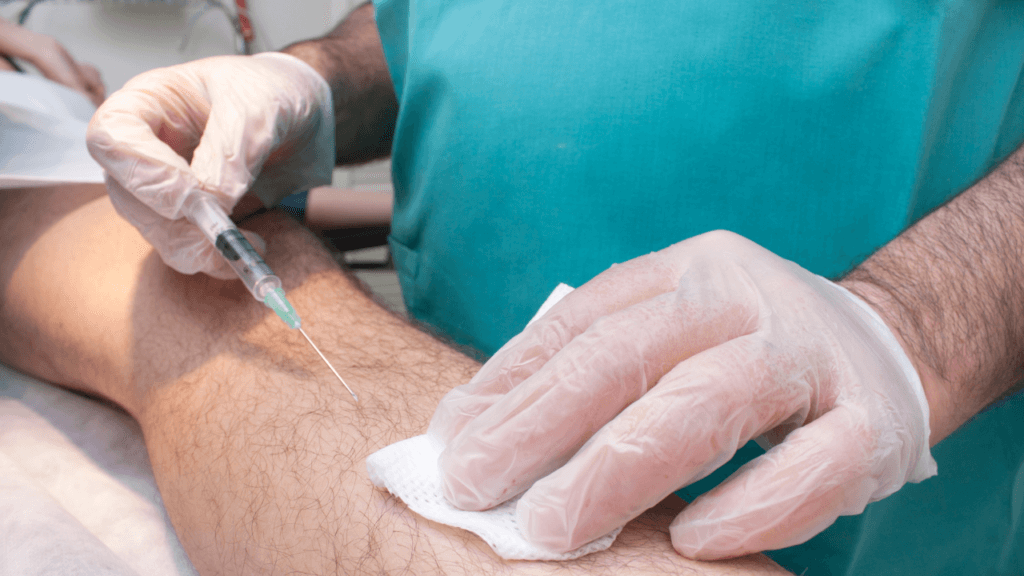
While anesthesia is commonly used on many patients without complications, there are always potential risks when you are “going under” for surgery. One potential complication that could qualify for an intubation injury anesthesia malpractice claim is if a nerve injury occurs.
If you have experienced a nerve injury from anesthesia, the experienced personal injury attorneys at Rosenblum Law can recover the compensation you deserve. Contact us today for a free consultation.
How Does Anesthesia Malpractice Cause Injury?
Anesthesia errors can cause nerve damage either directly or indirectly. Direct nerve damage can occur if there is a mistake in the placement of the anesthesia needle, such as placing the needle in a way that damages a cluster of spinal nerves. Alternatively, if the needle is already in place and the patient is repositioned, then it’s possible that the new position could pinch a nerve or restrict blood flow to the nerves.
Indirect nerve damage can happen as a result of anesthesia or if your body doesn’t react well to the medication. In rare cases, the surgery site malfunctions or shuts down as a result of this medication.
About 10-50% of patients suffer some type of nerve injury after surgery, depending on the type of surgery. The percentage is higher for spinal surgeries. Often this nerve damage can be treated, but some patients have life-long adverse effects.
Just because an anesthesia injury occurs doesn’t necessarily mean you have grounds for a malpractice case. The best solution is to talk to an experienced medical malpractice attorney for evaluation and recommendations for your situation.
It’s necessary to show that the medical provider was negligent or made a mistake with the administration of the anesthesia. Or, if the provider had prior knowledge that anesthesia is a problem for you but still administered it, then it’s possible that they might be held liable for your injuries.
Classes of Nerve Injuries
There are three classes of nerve injuries.
- Neurapraxia is the mildest of nerve injuries. It is fairly easy to recover from and doesn’t cause any lasting damage.
- Axonotmesis is a more serious nerve injury that is still recoverable, but recovery takes longer than with neurapraxia. Surgery is sometimes necessary, but not always.
- Neurotmesis is the most severe type of nerve injury and occurs when the nerve is completely ruptured. Often, people with neurotmesis do not feel any pain because their nerve damage is so extensive.
Symptoms of Nerve Injury After Anesthesia
If nerve damage occurs during or after anesthesia, symptoms might include:
- Weakness
- Numbness
- Muscle atrophy
- Feeling of pins and needles
- Loss of coordination and balance
- Hypersensitivity
- Paralysis
- Pain
- Digestive issues
- Incontinence
- Problems with motor function
Sometimes these symptoms will dissipate soon after the surgery. Other patients experience life-long, debilitating issues. Not only can these anesthesia injuries impact quality of life, but it can be frustrating to knowingly live with incurable damage as the result of a doctor’s mistake.
What Can Be Recovered?
If someone decides to file a medical malpractice claim for an anesthesia injury, there are mental and physical aspects for which they can receive compensation. For example, it is relatively easy to put a dollar amount on medical bills, expenses, and lost wages.
If the victim’s quality of life has been impacted, their attorney will also help negotiate compensation for pain and suffering. Even though this is a bit more difficult to quantify, it is still worth including in the malpractice claim.
How to Prove Anesthesia Malpractice
To prove anesthesia malpractice, the plaintiff must prove three elements.
- Duty: The defendant had a patient-provider relationship with the plaintiff and thus owed the plaintiff a professional duty of care. If there is no provider-patient relationship, there is no duty of care.
- Breach: The defendant breached this duty by treating the plaintiff in a manner that clearly fell short of the applicable standard of care. The standard of care is that which is generally accepted in the medical community for a given treatment and situation.
- Injury and causation: It’s not enough to show that the defendant breach the standard of care; it must also be shown that it’s more likely than not that this breach directly caused the plaintiff’s injury or injuries.
FAQs
Ulnar nerve injury anesthesia problems are common after general anesthesia. The Ulnar nerve can be injured by compression due to the weight of the body against the operating table.
Nerve damage during surgery can result in a variety of issues that affect a person’s function and sensations, including numbness, weakness, and/or pain in the affected area.
Some symptoms of nerve injury happen immediately after a patient wakes up from anesthesia. Other times, it takes days or weeks before symptoms are fully apparent.








 888-815-3649
888-815-3649
